Table of contents
- What is forex, and what is forex trading?
- Why is the forex market so popular?
- Types of pairs in the forex market
- How does currency trading work?
- What are bid and ask prices in forex?
- What is the spread in forex trading?
- What are pips in forex?
In the world of financial markets, forex has a special place. It is the world's most popular and biggest financial market, and as of April 2022, it has an average daily trading volume of USD 7.5 trillion. But what does forex mean, and how can you trade it? In this article, we’ll walk you through the basics of the forex market and the terms you need to know to start forex trading.
What is forex, and what is forex trading?
Forex, commonly referred to as FX, stands for the foreign exchange market. It’s a global marketplace where dozens of currencies are converted into one another for various purposes, such as international trade, tourism or personal gain. Due to its nature, forex trading involves a wide range of participants in this exchange process – governments, banks, multinational corporations, institutional investors, retail traders and even regular people. In fact, anyone who has ever travelled abroad and exchanged their home country’s currency for a local currency of their destination has done a transaction on a foreign exchange market.
Why is the forex market so popular?
There are many reasons why the currency market is so popular among online traders. Here are some of its main benefits:
Easier to follow
There are only a few currencies that most traders follow – these include the US dollar, Euro, and British pound. Other favoured but less frequently traded currencies are the Canadian, Australian, and New Zealand Dollars, and the Japanese Yen. As there are only a handful of popular currencies to focus on, it can help make it easier for traders to develop a deeper understanding of their behaviour and the factors that influence their movements.
Liquidity
The large number of participants and transactions bring high liquidity to forex trading, resulting in very low trading costs. And the ever-present supply and demand makes trading on leverage highly accessible. The latter allows good traders even with a small amount of capital to extract value from the forex markets, something that’s difficult to do when trading stocks.
Volatility
Forex prices can be influenced by various factors, which often cause high volatility and, as a result, numerous trading opportunities. Take a value stock as a comparison, it may hardly move some days, making it difficult to day trade. This is not the case with Forex trading, and you can find opportunities anytime during the day, whether it be after, before, or during work hours.
Round-the-clock access five days a week
Due to its decentralisation, forex transactions can be carried out at any time, except during the weekend. There is no centralised exchange, instead central banks, large banks, hedge funds, and retail brokers have built electronic networks, and deal directly with each other to facilitate trading outside traditional trading hours.
How does forex work?
When a forex trader exchanges a currency, you sell it and buy another one. Since there are always two currencies involved in this process, forex instruments are quoted in pairs – for example, EUR/USD or GBP/USD. The first currency is referred to as the base, and the second one is called the quote.

Types of pairs in the forex market
Forex pairs are divided into three large groups depending on what currencies are included in them.
Major currency pairs
Major pairs include the currencies of the most developed countries traded against the USD. The US dollar is always present in these pairs as the base or quote currency because it is an official reserve currency worldwide, meaning it is widely used in international trade and held as a reserve by central banks across the world. It makes USD the dominant currency in forex and other markets like commodities that are also traded against it. Some of the most popular major pairs are EUR/USD, GBP/USD and USD/JPY.
Minor currency pairs
Minor pairs also include currencies of large economies but are not tied to the USD – EUR/GBP, EUR/CHF or GBP/CAD, for example.
Exotic currency pairs
Exotic pairs usually consist of one currency of a major economy traded against the currency of a developing country. Some examples are AUD/MXN, USD/HKD and GBP/ZAR.
How does currency trading work?
The value of a forex pair indicates the value of a base currency against the quote currency. In other words, it shows how many units of the quote currency you can get for 1 unit of the base currency. This is also called an exchange rate.
For example, the EUR/USD currency pair exchange rate at the time of writing was 1.02839, which means for 1 euro, you would get 1.02839 US dollars.

It is important to note that since the forex market is decentralised, the exchange rate may vary from one broker or bank to another.
When it comes to online trading, brokers source their exchange rates from a group of establishments called liquidity providers – usually banks and other large financial institutions and display them as bid and ask prices.
What are bid and ask prices in forex?
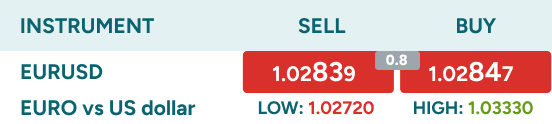
In forex trading, you have probably come across "bid" and "ask" prices. Think of the "bid" as the price you'll receive when you want to sell a currency. The "ask" is the price you'll pay when you want to buy. For example, if you're looking at EUR/USD, the "bid" tells you how many US dollars you'll receive for selling 1 Euro, while the "ask" represents how many US dollars you need to spend to buy 1 Euro. As you can see in the image below, you would receive 1.02839 USD for selling one Euro, while if you were to buy one Euro, you would need to pay 1.02847. This buy price is slightly higher than the sell price because of the spread, which is the difference between the “bid” and “ask” prices.
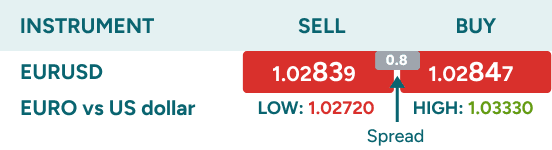
What is the spread in forex trading?
A spread in forex trades means the difference between the buy and sell prices that represents the transaction cost of every currency pair. Whether you buy or sell a currency, you will always be charged this amount upon opening a trade. The spread is what your broker earns for enabling you to trade. It is a markup, the same way as retailers adds a markup in any other product. However, the high competition in the forex markets ensures it’s the cheapest financial market to trade.
In the image below we see that the cost of trading is 0.8, for a 100,000 Euro transaction the cost would be 8 USD, making it unbeatably cheap.
When you open a trade, the spread is deducted from the start. In a winning trade, the spread cost is deducted from a profit, and in a losing one, it is added to the loss.
It’s important to note that a spread directly depends on the liquidity of a currency pair. For example, the most liquid pairs (majors) usually have very tight spreads, meaning traders can open positions at a lower cost and make a profit faster if the market moves in their favour. Minor pairs are traded less often and have wider spreads, slightly increasing the trading cost, and exotic currency pairs have the widest spreads.
The spread amount also varies from broker to broker and can even be different depending on the account type within the same broker. For example, if you trade forex with ThinkMarkets, a Standard account will give you access to tight spreads – just a few pips, but if you choose a ThinkZero trading account, most pairs will have 0 spreads.
What are pips in forex?
In forex trading, pip stands for percentage in point or price interest point. It is the smallest one-digit movement of a currency’s price measured by the fourth decimal point and used to calculate a spread.
Here is a little graphic to help you understand how the price of a currency works:
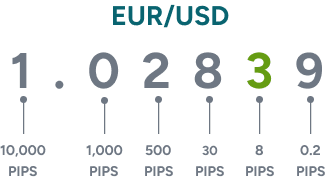
Forex pairs that have Japanese yen as a quote currency are displayed only until the third decimal point, so the pip is measured by the second one.

To calculate a spread, you need to subtract the sell price from the buy price. In our previous example, the spread is:

On ThinkMarkets’ proprietary platform, ThinkTrader, the spreads are displayed within each price quote for your convenience, so you don’t need to calculate them.
Now, your next question may be how to calculate your profit or loss in pips when you trade forex and how to trade forex in the first place. Head over to our next article, where we discuss it in detail. You can also create a demo trading account on ThinkTrader to apply your newly obtained knowledge in practice.
FAQs
How much do you need to start trading forex?
There is no minimum amount required to start trading forex. However, some brokers may impose minimum deposit requirements. With a Standard account on ThinkMarkets there is no minimum deposit – you can trade forex with as little as a few dollars.
When to buy and sell in forex?
There are many ways to identify trading opportunities on forex. Check out our “What affects foreign exchange rates” article to know more.
How long does it take to learn forex?
Like any other new skill, the amount of time required to learn forex trading depends on individual skills and on how much time you will dedicate to it. With the right approach you can grasp the basics quite fast and then move to the advanced strategies, practicing trading on a demo account continuously.
How old do you have to be to trade forex?
You have to be at least 18 years old to engage in forex trading activities.





